Download document () of 20
Download
You have exceeded the download limit
In the world of commercial vehicle maintenance, staying ahead of the curve is not just a preference – it's a necessity. ServiceRanger® 4 can help make sure your Eaton Cummins automated transmissions operate effectively and efficiently. How exactly does ServiceRanger® work and what sort of problems does it help maintenance managers like you solve?
To answer these questions from an insider's perspective, we had Joshua Deshazer, an Eaton Cummins Customer Experience Representative, walk us through ServiceRanger 4 screen by screen in simulation mode.
Home Screen
There are four main areas on the home screen:
If you are a technician who works on many trucks makes, the connection settings can vary by OEM. The connection settings featured in ServiceRanger 4 makes this easy to set up and save various trucks so you can successfully communicate with the truck. This is a big time saver!
Once you've identified your correct connection settings, click Connect. It takes a few seconds to establish the connection with the transmission control module. This is the screen you will see (less the simulation mode warning).
A notification lets you know that you’re connected to a particular model of transmission and if there are any active faults detected.
Once you click OK, it brings you back to the main home screen where you can see your status. It will tell you if you are connected to a transmission and what transmission you are connected to.
At the top of screen is your main menu button that lists your options:
Now, we’ll walk you through how to use each menu option.
Fault Codes
One of the most common uses of ServiceRanger 4 is to find fault codes. You will see the active fault codes for your truck, including engine, braking system, and transmission to help you get a bigger picture of what's going on with the truck.
Once you have a transmission fault selected, you can click the green arrow dropdown option on the left of the screen to see the troubleshooting button. This takes you to our service product literature and it will walk you through step-by-step on how to resolve this fault code or get to the bottom of the problem.
Data Monitoring
Another great feature of ServiceRanger 4 is data monitoring. This is probably one of the more underutilized features. If there is an issue that isn't producing a fault code, but you recognize the problem through its symptoms, you can use this area to monitor live data from the transmission. In this case, we're looking at shift rail positions. The screen shows that our command is causing an error. If you were a technician working on this, you would be able to recognize that rail D was having a problem even without a fault code.
Another common issue is when a transmission won't go into gear from neutral. The transmission will not go into neutral unless it can recognize that a driver is sitting in the seat. It does this by monitoring if the driver has pressed the brake pedal and selected Drive on the shift stalk. Data monitoring will allow you to test what happens when the driver puts their foot on and off the brake. This setting should say it is depressed when the foot is on the brake pedal and should change to released when the foot is off. This helps you identify if the “transmission issue” is with the brake pedal.
Software Updates
Service Activity Reports
Technicians use service activity reports when they have already looked at the live data and done the service routines. This is the next step when they can’t quite figure out the issue with the truck.
Clicking on the service activity report button prompts you to fill out the requested information. Once you’ve filled out all the red boxes, you click start. This will download all information that the transmission they are currently connected to: fault codes, configurations, software levels, and transmission TA number. It then gives a vehicle performance analysis with totals of how long the transmission has been in each individual gear, how many actuations of the clutch there have been, etc.
This screen shows what the service activity report looks like to the technician. Next, you need to click the "Send to Eaton” button on the top right of the screen. If you have an internet connection, this will upload your report to our service activity report database. When you call our tech support line, your customer service representative will be able to see your report and walk you through your next steps.
Any service activity reports you make will be listed at the top.
If you ever need the type of information from these reports but you are not connected to a truck, you can go to our product information library. On this screen you can search by transmission model and description and pull up the service literature for that product.
If you are a fleet shop manager and one of your drivers calls with a transmission problem, you don’t need to be connected to the transmission to be able to help. The driver can give you the generic fault code description on the dash so you can take that fault description and go into the troubleshooting guide without being connected to the truck. By entering that fault description, you can figure out if this is something that they need to pull over immediately for, if they can keep driving, or if they should go straight to a repair facility.
Configurations:
Neutral Cost Mode
Mode Configurations & Urge to Move
PTO functionality
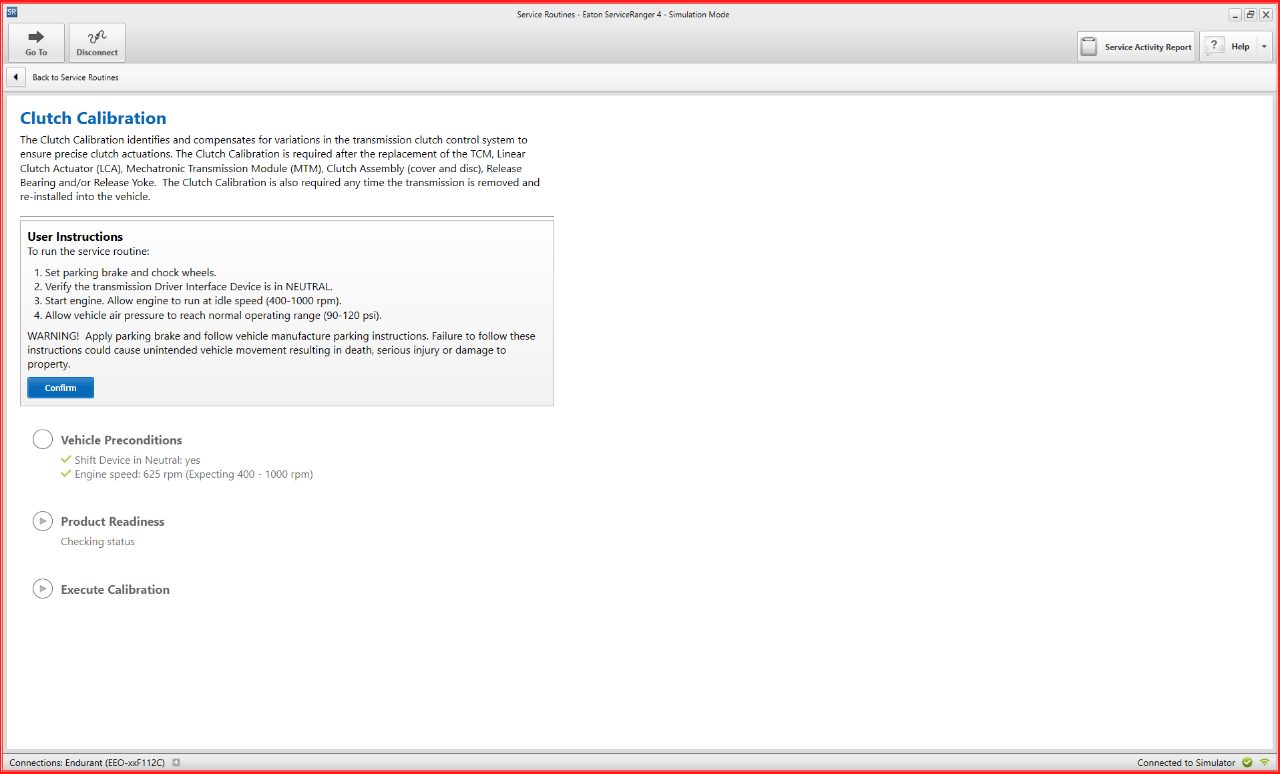
Clutch Calibration
You can calibrate your clutch from the configurations screen which needs to be done when your clutch wears out and you replace it.
Over the life of a clutch, the transmission control module saves its position data points. This ensures a smooth, consistent operation. The TCM has to adjust as the clutch wears and does not automatically know that a new clutch has been installed into the truck. Performing this clutch calibration clears out old saved data points and forces it to learn a new baseline set of clutch points.
To perform a clutch calibration in ServiceRanger 4, follow these concise steps.
1. Follow the user instructions in the center of the screen and navigate to the clutch menu.
2. Consult the service manual for specific guidance on torque specifications and step-by-step instructions for proper transmission removal. The manual directs you to connect to Service Ranger and execute a clutch calibration in the service routine section.
3. Ensure the engine is running during this process, as attempting calibration with the engine off will trigger an alert due to insufficient engine speed (below 400 RPM).
4. Follow the on-screen instructions: set the parking brake, chock the wheels, ensure the transmission gear selector is in neutral, start the engine, confirm air pressure, and hit "confirm."
5. Once all preconditions are met, click “execute calibration.”
This process takes about a minute. Upon completion, the system will indicate success or highlight any detected errors, providing valuable feedback for effective clutch calibration. These steps apply universally to all ServiceRanger 4 service routines.